Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are becoming increasingly important for businesses to effectively manage and integrate various aspects of their operations. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of ERP, its key features, benefits, and implementation challenges.
We will also cover how ERP systems work, how to choose the right ERP software for your business, and the future of ERP systems. When you read our article from the beginning to the end, you will have a wide range of knowledge about ERP.
Contents
- 1 What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
- 2 History of ERP
- 3 Why Is ERP Important?
- 4 What are the Features of ERP?
- 5 12 Benefits of Implementing ERP Systems
- 6 Challenges of ERP Implementation
- 7 How Does an ERP System Work?
- 8 The Future of ERP
- 9 How to Select the Right ERP System
- 10 Enterprise Resource Planning Related Videos
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software application that allows businesses to integrate and manage various core processes, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer relationship management (CRM), in a centralized system.
ERP systems provide organizations with a unified and real-time view of their operations, allowing them to streamline and automate their business processes, improve efficiency, and make informed data-driven decisions. By consolidating data from different departments and functions, ERP enables seamless communication and collaboration within an organization, facilitating better coordination and resource allocation.
With ERP, businesses can standardize and automate routine tasks, eliminate manual or redundant processes, and optimize operations across different units or locations. The software often includes modules for functions such as accounting, inventory management, procurement, project management, sales, and marketing, providing a comprehensive solution for managing all aspects of a business.
ERP systems are designed to be flexible. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries or businesses. They typically offer a range of features and capabilities, including centralized databases, analytics and reporting tools, workflow automation, customer and supplier management, inventory tracking, and financial planning and forecasting.
Moreover, ERP solutions provide businesses with improved visibility and control over their operations, enabling them to effectively monitor performance, track key metrics, identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement. The integration of various functions and access to real-time data also enhance the accuracy and timeliness of information, enabling faster response to changing market demands or customer needs.
In summary, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software application that helps businesses integrate and manage various core processes in a centralized system. With ERP, organizations can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions by providing a unified view of their business functions.

History of ERP
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software system used by organizations to manage and integrate various business functions and processes.
- The history of ERP dates back to the 1960s when it emerged as Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems, primarily used for inventory management in manufacturing industries.
- In the 1980s, MRP systems evolved into Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) systems, which expanded their functionality to include other aspects of the manufacturing process such as capacity planning and scheduling.
- In the late 1980s and early 1990s, ERP systems emerged as the next generation of enterprise management software. These systems integrated various business processes beyond manufacturing, covering areas such as finance, sales, human resources, and supply chain management.
- ERP systems gained popularity in the 1990s as businesses recognized the benefits of centralizing data and streamlining processes across different departments.
- The late 1990s and early 2000s saw significant growth in the ERP market, with several software vendors offering their versions of ERP systems.
- With advances in technology, ERP systems have seen continual enhancements, integrating new features such as business intelligence, customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management.
- Today, ERP systems are a crucial tool for organizations of all sizes and industries. They provide a comprehensive solution to manage and optimize their resources, enhance decision-making, and improve operational efficiency.

Why Is ERP Important?
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is crucial for organizations across industries. Here are some reasons why ERP is important:
- Streamlined operations: ERP integrates various departments, functions, and processes into a single unified system. This streamlines operations by ensuring efficient communication, collaboration, and data sharing across the organization.
- Improved productivity: ERP eliminates manual and repetitive tasks by automating them. This improves productivity as employees can focus on more value-added activities, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Enhanced decision-making: ERP provides real-time data and insights, enabling better decision-making at all levels of the organization. Managers can access accurate and up-to-date information, helping them make informed choices to drive business growth.
- Optimized resource allocation: With ERP, organizations can effectively manage their resources, including inventory, finances, and human capital. This leads to better utilization of resources, minimizing waste, and maximizing profitability.
- Increased customer satisfaction: ERP allows organizations to improve customer service by providing access to comprehensive information about customers, their orders, and preferences. This helps in delivering personalized experiences, resolving issues quickly, and fostering long-term customer relationships.
- Improved compliance: ERP systems often include regulatory compliance capabilities. This ensures that organizations adhere to industry-specific regulations and requirements, reducing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
- Scalability and flexibility: ERP systems are designed to accommodate growth and change. They can readily adapt to evolving business needs, allowing organizations to scale up or down as required and seamlessly integrate new processes or modules.
In summary, ERP is essential as it streamlines operations, improves productivity, enables better decision-making, optimizes resource allocation, enhances customer satisfaction, ensures compliance, and offers scalability and flexibility. Organizations that embrace ERP gain a competitive advantage by fostering efficiency, innovation, and growth.

What are the Features of ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a wide range of features to help streamline business processes and improve overall efficiency. Some key features of ERP include:
- Integration: ERP integrates various departments and functions within an organization, such as finance, human resources, procurement, inventory management, and production. This allows for improved collaboration and communication across departments.
- Centralized Data: ERP centralizes all relevant data in one location, making it easier to access and analyze information. This helps decision-makers gain real-time insights and make data-driven decisions.
- Automation: ERP automates repetitive tasks and processes, reducing manual efforts and minimizing errors. This helps increase productivity and efficiency.
- Scalability: ERP systems are designed to meet the growing needs of companies. They can easily scale up or down according to the requirements of the organization and allow for flexible growth.
- Customization: ERP systems can be customized by companies in line with their business needs. With this feature, the software becomes compatible with the organization’s processes and workflows.
- Reporting and Analytics: ERP provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling organizations to monitor key performance indicators, track trends, and generate insightful reports. This helps in making informed business decisions.
- Security: ERP systems have built-in security features to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of business information.
- Mobile Access: Many ERP systems offer mobile access, allowing users to access and interact with the system from anywhere. This facilitates remote work and enhances user convenience.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Some ERP systems have integrated CRM functionality, which helps businesses manage customer relationships, track sales, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Overall, ERP systems provide a comprehensive suite of features to streamline business operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.

12 Benefits of Implementing ERP Systems
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems streamline business processes, eliminate manual tasks, and automate workflows, resulting in increased efficiency and higher productivity levels.
- Enhanced Data Security: ERP systems provide robust data security measures to protect sensitive business information, restrict unauthorized access, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Real-time and Accurate Reporting: With ERP systems, companies can generate real-time reports on various operational aspects, enabling better decision-making based on accurate and up-to-date information.
- Increased Collaboration and Communication: ERP systems promote collaboration and communication among different departments and teams, facilitating a seamless flow of information and fostering better teamwork.
- Cost Savings: By eliminating redundant processes, optimizing inventory management, and reducing manual errors, ERP systems help businesses save costs and improve overall financial performance.
- Better Customer Service: ERP systems enable businesses to provide exceptional customer service by giving quick access to customer data, and order history, and enabling efficient order processing and delivery.
- Scalability and Flexibility: ERP systems are designed to accommodate business growth and scalability, allowing companies to easily add new modules, users, or functionalities as their needs evolve.
- Integration of Business Functions: ERP systems integrate various business functions, such as finance, sales, inventory management, and human resources, ensuring a seamless flow of information across the organization.
- Enhanced Decision-making: ERP systems provide tools for data analysis and reporting, empowering decision-makers with accurate insights and enabling informed strategic decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems help businesses comply with industry-specific regulations, tax laws, and financial standards by providing built-in compliance features and automated reporting capabilities.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Management: ERP systems offer tools for efficient supply chain management, enabling businesses to optimize procurement, inventory control, and distribution processes.
- Improved Business Visibility: ERP systems provide a centralized platform that gives businesses a holistic view of their operations, enabling better monitoring, analysis, and control of key business metrics.
In summary, implementing an ERP system brings numerous benefits to businesses, including improved efficiency, enhanced data security, real-time reporting, cost savings, better customer service, scalability, and flexibility. It also facilitates collaboration, integration of business functions, enhanced decision-making, regulatory compliance, streamlined supply chain management, and improved visibility into business operations.

Challenges of ERP Implementation
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can be a complex and challenging process. Organizations often face several obstacles when it comes to successfully implementing ERP solutions. Some of the key challenges include:
- Resistance to change: One of the major hurdles in ERP implementation is the resistance to change from employees within the organization. People tend to be comfortable with familiar processes and may initially resist adopting new systems and workflows. It is crucial to address this resistance through effective change management strategies and comprehensive employee training programs.
- Data migration and integration: Integrating existing data from different sources into the new ERP system can be a time-consuming and complex task. Data needs to be cleansed, standardized, and mapped to fit the new system’s structure. This process requires careful planning, expertise, and robust data migration tools to ensure accurate and seamless data transfer.
- Customization and configuration: Organizations often have unique workflows and specific requirements that may not be fully addressed by out-of-the-box ERP solutions. Customization and configuration can be challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of the ERP system’s capabilities, potential impact on other modules, and careful consideration of future upgradability.
- Resource allocation: Implementing ERP systems requires significant resources in terms of time, money, and personnel. Organizations need to allocate dedicated teams, including project managers, IT specialists, and subject matter experts, to ensure the successful deployment of the ERP solution. Additionally, budgeting for licenses, hardware, infrastructure upgrades, and ongoing maintenance costs is essential.
- Software selection: Choosing the right ERP software is crucial to the success of the implementation. Organizations need to carefully evaluate software based on factors such as their industry expertise, solution functionality, support services, scalability, and long-term viability. Making the wrong software choice can lead to implementation issues, poor support, and future limitations.
- Training and user adoption: Adequate user training is vital for successful ERP implementation. Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees can effectively use the new system. Lack of training can lead to low user adoption, resistance, and errors, ultimately hindering the benefits that ERP systems bring.
Overcoming these challenges requires meticulous planning, effective change management, clear communication, and collaboration between stakeholders. Organizations need to have a well-defined roadmap, engage employees at all levels, closely monitor progress, and continuously refine the implementation strategy to ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP system.

How Does an ERP System Work?
ERP system works by integrating various business functions and processes into a unified system to streamline operations and improve overall efficiency. The working system of ERP is generally as follows;
- Centralized Database: An ERP system utilizes a centralized database that stores all relevant data and information across different departments and functions of an organization. This allows for easy access, real-time updates, and a single source of truth for all users.
- Modules and Integration: ERP systems consist of various modules that correspond to different areas of a business, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and sales. These modules are interconnected and integrated, enabling seamless data flow and communication between departments.
- Data Input and Capture: Users input data into the ERP system through user-friendly interfaces or automated data capture methods. This can include manual data entry, importing data from external sources, or integration with other systems within the organization.
- Data Processing and Analysis: Once data is captured, the ERP system processes and analyzes it according to predefined rules and workflows. This includes performing calculations, generating reports, and providing data insights to aid in decision-making processes.
- Automation and Workflow Management: ERP systems help automate various business processes by defining and implementing workflows. These workflows ensure that tasks and operations are carried out systematically and efficiently, minimizing manual intervention and reducing the risk of errors.
- Collaboration and Communication: ERP systems facilitate collaboration and communication among different teams and departments within an organization. This includes shared calendars, task assignments, document sharing, and real-time messaging, ensuring effective coordination and smooth information flow.
- Monitoring and Reporting: An ERP system provides real-time monitoring and reporting capabilities, giving users instant access to key performance indicators (KPIs), dashboards, and analytics. This helps in tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and making data-driven decisions to improve overall performance.
- Security and Data Privacy: ERP systems ensure data security and privacy by implementing robust access controls, encryption techniques, and regular backups. This protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Overall, an ERP system eliminates the need for separate standalone systems, streamlines operations, enhances data accuracy, and improves collaboration, all in a centralized and integrated environment.

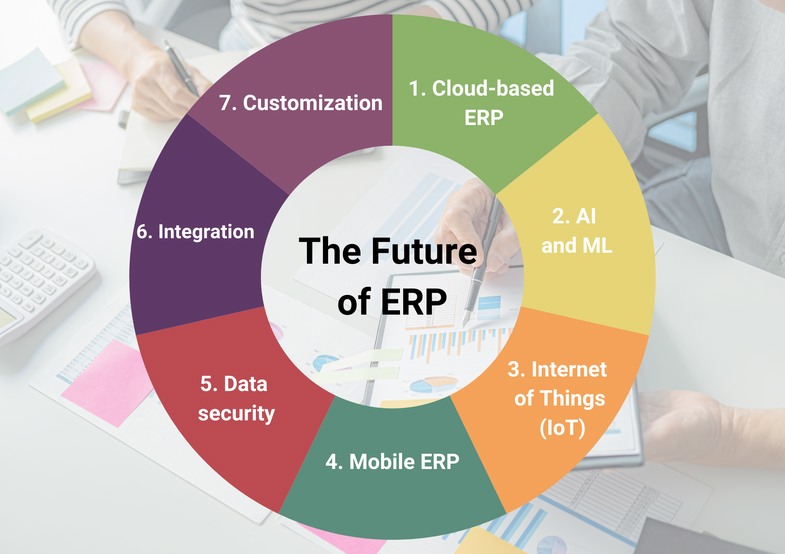
The Future of ERP
The future of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) looks promising, with several trends and advancements shaping its landscape. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Cloud-based ERP: Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, and ERP systems are no exception. Cloud-based ERP offers increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. It allows businesses to access real-time data from anywhere, making remote work and collaboration more seamless.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming ERP systems by enabling intelligent automation and predictive analytics. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make data-driven recommendations, leading to better decision-making and streamlined processes.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT integration with ERP systems allows the collection of real-time data from connected devices, enabling smarter inventory management, predictive maintenance, and improved supply chain visibility. IoT-enabled ERP systems can optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Mobile ERP: Mobile devices are ubiquitous, and the future of ERP lies in their seamless integration. Mobile ERP applications empower employees to access and update data on the go, enhancing productivity, collaboration, and decision-making. Mobile ERP also enables remote monitoring and control of essential business processes.
- Enhanced data security: As data becomes more critical, the future of ERP depends on robust security measures. ERP vendors are increasingly implementing advanced encryption techniques, multi-factor authentication, and other security protocols to protect sensitive business data from cyber threats.
- Integration with emerging technologies: ERP systems are expected to integrate with emerging technologies like blockchain and augmented reality (AR). Blockchain can add transparency, security, and traceability to supply chain processes, while AR can enhance productivity by providing real-time visual guidance to users.
- Personalization and customization: The future of ERP lies in offering personalized and customizable solutions. Businesses will have the flexibility to tailor their ERP systems to meet specific industry requirements, workflows, and user preferences, enabling better user adoption and increased efficiency.
In conclusion, the future of ERP holds great potential. Cloud-based solutions, AI and ML, IoT integration, mobile accessibility, enhanced security measures, and integration with emerging technologies will drive the evolution of ERP systems, making them more agile, intelligent, and customizable for businesses across various industries.
How to Select the Right ERP System
Choosing the right Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system for your organization is a crucial decision that requires careful consideration. Here are the key elements to consider when choosing an ERP system:
- Business requirements: Begin by assessing your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Identify the core processes that the ERP system should support, such as finance, inventory management, human resources, or customer relationship management.
- Scalability: Consider the long-term growth and expansion plans of your organization. Choose an ERP system that can easily adapt to your changing business needs and accommodate future growth without the need for major software upgrades.
- Integration capabilities: Evaluate the ERP system’s compatibility with your existing software applications and systems. Ensure that it can seamlessly integrate with other critical systems such as accounting software, CRMs, or supply chain management tools.
- Ease of use: Enterprise resource planning software should be user-friendly. Choose an ERP system that has an intuitive interface and requires minimal training for employees to navigate and use it effectively.
- Customization options: Assess if the ERP system allows customization to meet your specific business needs. This is important as every organization has unique processes and requirements that may not be fully addressed by an out-of-the-box solution.
- Vendor support: Evaluate the vendor’s reputation, experience, and level of customer support. Ensure that they offer ongoing technical support, and regular software updates, and are responsive to your organization’s needs in case of any issues or concerns.
- Data security: Today, data security is of utmost importance. Ensure that the ERP system follows industry-standard security protocols and offers features such as data encryption, user access controls, and regular data backups to protect your sensitive business information.
- Cost considerations: Evaluate the overall cost of the ERP system, including upfront implementation costs, ongoing maintenance fees, and any required hardware or software upgrades. Consider both the short-term and long-term costs to make an informed decision.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that you select the right ERP system for your organization, one that aligns with your business goals, streamlines your processes, and enables future growth and success.
Enterprise Resource Planning Related Videos
We also want to share with you videos about enterprise resource planning. This video answers your questions in the best way. You can click HERE for more videos.
