Kaizen, one of the foundations of the Japanese quality of work and personal life, is the most well-known continuous improvement methodology. With this continuous improvement methodology, you can create positive changes in both your business and personal life.
In our article, we focused more on business life while explaining kaizen, but you can also adapt this information to your own life. After reading our article, you can have detailed information about kaizen and continuous improvement. After applying it in your business life, you can witness positive changes.
Contents
- 1 What is Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)?
- 2 What are the Benefits of Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)?
- 3 The Kaizen Cycle in Continuous Improvement
- 4 What are Continuous Improvement Methodologies?
- 5 What is a Kaizen (Continuous Improvement) Process?
- 6 What are the Principles of Kaizen?
- 7 5 Continuous Improvement Examples
- 8 Videos Related to Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
What is Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)?
Kaizen, also known as continuous improvement, is a term that we encounter in every moment of life but is little known. The word Kaizen is a Japanese word. Kai means “change” and zen means “good”. Kaizen, which includes everyone, every event, every moment, is an improvement and lean manufacturing technique that aims to continuously achieve better. That is why it is also known as continuous improvement.
Kaizen always prioritizes the process. In our daily lives, we encounter many problems, complex events, and tasks. In such situations, it is important to look for ways to improve. Let’s explain with an example; Let a chair be produced only according to durability criteria. While designing and producing this table, the main goal should be to try to answer and improve questions such as what features can be added, how it would be useful, and what can be done to make the customer like the product. In other words, development here is continuous and unlimited.
The origins of Kaizen date back to the Second World War. It was first used by the quality units of the Japanese automotive manufacturer Toyota. At the time, people working in quality units focused on preventing defects in Toyota’s production system. Around the same time that the Kaizen philosophy was being introduced in Western countries, Masaaki Imai published a book in 1986 entitled “Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success” was published in 1986. This book became very popular in the business world. As time passed, Kaizen practices became known as Kaizen philosophy.

What are the Benefits of Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)?
Kaizen, or continuous improvement, provides many benefits in every sense. These;
- Increased Productivity: Through continuous evaluation and improvement of processes, Kaizen leads to increased efficiency in the workplace. This results in less wasted time, higher productivity, and ultimately cost savings for the organization.
- Employee Engagement: Kaizen fosters a culture of continuous learning and growth by encouraging employees at all levels to participate in the improvement process. This engagement increases morale, job satisfaction, and overall employee retention.
- Quality Improvement: Kaizen, a continuous improvement methodology, helps improve the quality of products or services by focusing on making small incremental changes. This commitment to quality is crucial to meeting customer expectations and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
- Cost Savings: Continuous improvement through Kaizen can lead to cost reductions by eliminating waste, streamlining processes, and optimizing resources. This financial benefit contributes to the organization’s bottom line.
- Innovation: The emphasis on constantly looking for better ways to do things encourages innovation within the company. By encouraging employees to think creatively and suggest improvements, Kaizen creates a culture of innovation and adaptability.
- Risk Reduction: Kaizen reduces the likelihood of major problems or failures in the future by identifying and addressing issues early on. This proactive approach minimizes risks and ensures smoother operations in the long run.
- Customer Satisfaction: Kaizen focuses on meeting customer needs by improving processes and delivering higher-quality products or services. This is why customer satisfaction levels typically increase. Customers who are satisfied with the product or service are more likely to buy again and recommend the business to others.
- Competitive Advantage: Practicing Kaizen provides a competitive advantage by constantly improving and adapting to market demands. This flexibility and agility enables organizations to stay ahead of their competitors and thrive in rapidly changing business environments.

The Kaizen Cycle in Continuous Improvement
The Kaizen philosophy is generally applied in a 7-step cycle, focusing on sustainable improvement. This cycle includes the following steps:
- Employee Involvement: Enlist the help of employees to participate in the process and ask them to help identify problems. This can make a significant difference in changes. Usually, specific people are assigned to collect and communicate information and this is how the system is organized.
- Identification of Problems: Using feedback from all employees, identify current and potential problems and list opportunities that can be associated with these problems.
- Solution Suggestions: Encourage employees to share their ideas. Employees may be hesitant to present their ideas. Provide a relaxed atmosphere and help them present creative solutions. A great solution(s) will surely come out of the ideas presented.
- Testing the solution: Implement the solution(s) selected in the all-participation meetings within a set timeframe. The testing process does not have to be long. You can end the testing phase when you think you have the necessary data on the subject.
- Analysis of Results: Create plans to ensure communication between levels at regular intervals. Ensure that participation is carried out in the best and most effective way. Measure the changes tried and evaluate their success.
- If there are positive results after improvements, adopt the solution across the business. At the same time, continue to implement it on an ongoing basis.
- Finally, make a list of newly identified problems. Improve the new problems in the list by following the steps above.
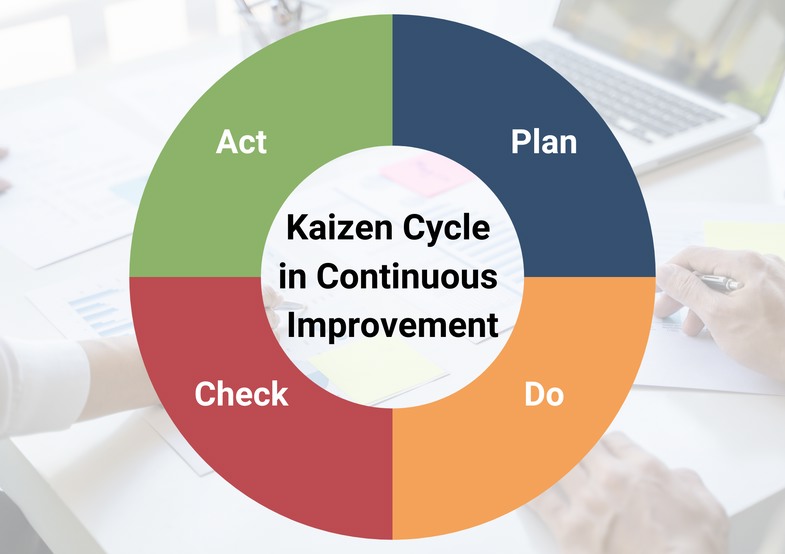
There are additional methods such as PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Measure), a 4-step approach based on the Kaizen philosophy. Let’s also briefly talk about the PDCA cycle.
- Plan: During this phase, organizations identify areas that require improvement and set specific goals for the improvement process. This step involves analyzing current processes, gathering data, and defining objectives.
- Do: In this phase, the organization implements the planned changes on a small scale. By executing changes on a small scale, organizations can observe the impact of the improvements without disrupting the entire system.
- Check: Organizations evaluate the results of the implemented changes in this stage. Data is collected and analyzed to determine whether the changes have resulted in the desired improvements. This step helps in understanding the effectiveness of the changes and identifying areas for further enhancement.
- Act: Based on the findings from the check phase, organizations take necessary actions to standardize the successful improvements. Standardizing the changes ensures that the improvements are sustained over time. If the expected positive results have not been achieved, it is necessary to return to the planning phase.
What are Continuous Improvement Methodologies?
- Kaizen: Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy that stands for continuous improvement. It aims to reduce waste and errors by making small, incremental changes to production and business processes.
- Kanban: Kanban is a visual work management system. It helps track and manage workflow using paper cards or electronic indicators.
- 5 Whys: This methodology, also known as root cause analysis, is a simple questioning technique used to find the root cause of a problem. By asking the question “Why?” five times in succession, the aim is to find the root of the problem.
- Fishbone Diagram: A fishbone diagram is used to visualize a problem’s possible causes. This diagram, which resembles the shape of a fish skeleton, helps to analyze the factors and sub-factors of the problem.
- Gemba Walks: This methodology is a Japanese term meaning that managers and leaders go to the production floor to observe problems and opportunities for improvement directly.
- Value Stream Mapping: Value stream mapping is the technique of creating a visual map of the production and delivery process of a product or service. It helps identify waste and bottlenecks.
- 5S: 5S stands for the five steps used to organize and clean up the workplace. 5S stands for Seiri (Sort), Seiton (Set), Seiso (Shine), Seiketsu (Standardize), Shitsuke (Sustain).
- Error Proofing: The technique of adding error-proofing mechanisms to production and business processes to prevent errors. In this way, errors are minimized.
- SIPOC Diagram: SIPOC is a diagram used to visualize the suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers of a process. It facilitates process analysis and improvement.
You may be interested: What is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)? Symbols, Tools and Examples

What is a Kaizen (Continuous Improvement) Process?
In the Kaizen process, there are several basic steps that organizations must follow to achieve continuous improvement. These steps are crucial for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and efficiency within a company. The main components of the Kaizen process are as follows:
- Identification of Areas: The first step in the Kaizen process is to identify areas within the company where improvements can be made. This may involve analyzing processes, systems, or workflows to identify inefficient or outdated areas.
- Setting Goals: Once areas for improvement have been identified, specific goals should be set to address these areas. These goals should be measurable, achievable, and aligned with the overall goals of the organization.
- Development of the Optimal Solution: Solutions tailored to the identified areas and objectives need to be developed. When developing solutions, achieving positive outcomes should be aimed for.
- Implementation of Solutions: After the development of solution methods, they should be implemented by the identified solution. This may involve redesigning processes, introducing new technologies, or providing training to employees.
- Monitoring Progress: It is crucial to monitor the progress of implemented changes. This may include tracking key performance indicators, gathering feedback from employees, or regularly reviewing improvement efforts.
- Review of Results: After a certain period, the results of improvement efforts should be reviewed to assess their impact on the organization.
What are the Principles of Kaizen?
The principles of kaizen, one of the continuous improvement methodologies, are as follows:
- Get rid of Assumptions: Instead of accepting the status quo without question, approach it with a belief that things can be improved.
- Be Proactive: Anticipate problems before they arise and adopt a proactive attitude to find solutions.
- Challenge the Status Quo: Instead of sticking to the status quo, always have the perspective that there is a better way.
- Let Go of Perfectionism: Set realistic goals and make progress by focusing on small, incremental improvements.
- See Mistakes as Opportunities: Treat mistakes as learning opportunities and ensure they are not repeated.
- Create a Participatory Environment: Create an environment where every employee can contribute and express their ideas freely.
- Apply Root Cause Analysis: Apply the most widely used technique of root cause analysis, the 5-cause analysis. Ask the question “why?” 5 times in a row to find the root cause of problems.
- Listen to Different Perspectives: Find more comprehensive solutions by getting information and ideas from different people. There is a saying in Turkey. “Two heads are better than one.”
- Think Creatively: Develop innovative solutions to increase functionality while reducing costs.
- Aim for Continuous Improvement: Never stop at “good enough”, always look for ways to do better.

5 Continuous Improvement Examples
1) Optimizing the Process
Example of continuous improvement related to process optimization;
The company creates a survey for customers with questions about demographics, project budgets, and timelines. After customers complete the survey, the company can instantly analyze the responses and provide customers with personalized offers.
2) Brainstorming
An example of continuous improvement related to brainstorming;
Team leaders organize a brainstorming session to identify the factors hindering sales. Team members share ideas on topics such as communicating with potential customers, making product presentations, and handling objections. At the end of the brainstorming session, the team identifies a set of strategies to increase sales.
3) Organizing the Team’s Work
Example of continuous improvement related to organizing the team’s work;
While reviewing the donor agreement, the employee notices the typo “donation amount”. He/she immediately corrects the mistake and makes a note to avoid repeating the same mistake in future contracts.
4) Reviewing Employee Performance
Example of continuous improvement related to reviewing employee performance;
A manager’s performance review shows that an employee needs improvement in presentation skills. The manager supports the employee’s development in this area by providing specialized presentation training and coaching.
5) Simplifying Purchasing Methods
Example of continuous improvement related to simplifying purchasing methods:
The e-commerce site offers various payment options such as credit card, bank transfer, and mobile payment. This appeals to customers with different payment preferences, making the purchase process easier and more accessible.
Videos Related to Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
We would like to suggest you a video about Kaizen (Continuous Improvement). You can learn about kaizen (continuous improvement) by watching this video. You can click HERE for more videos.
