Production planning is a crucial part of the production process. In this blog post, we will delve into the all ways of production planning. From its definition and importance to its history and common mistakes, we will cover everything you need to know about production planning. Whether you’re a business owner, a student, or simply curious about the world of manufacturing, this blog post will provide you with valuable insights into the world of production planning.
You may have little knowledge about production before you start production planning. Therefore, we recommend that you first take a look at our detailed article on production. » » What is Production? Meaning, Types and Factors
Contents
- 1 What is Production Planning?
- 2 History of Production Planning
- 3 Production Planning vs. Production Scheduling
- 4 Why is Production Planning Important?
- 5 Key Components of Production Planning
- 6 The Benefits of Effective Production Planning
- 7 Production Planning Process
- 8 5 Types of Production Planning
- 9 How to Production Planning?
- 10 Common Production Planning Mistakes
- 11 Videos Related to Production Planning
What is Production Planning?
Production planning is a crucial process that involves determining the most effective and efficient approach to producing goods or providing services. It is the backbone of any successful manufacturing or service-oriented organization.
At its core, production planning involves creating a detailed roadmap that outlines the steps and resources required to meet production goals. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including forecasting demand, scheduling production activities, managing inventory levels, and coordinating with various departments involved in the production process.
Production planning aims to optimize the use of resources, minimize costs, ensure timely delivery, and meet customer demand effectively. It involves making strategic decisions regarding production volume, production methods, equipment utilization, and staffing requirements. By carefully planning and scheduling production, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and maximize profitability.
Effective production planning requires a thorough analysis of market demand, capacity capabilities, and available resources. It involves aligning production schedules with sales forecasts and considering factors such as lead times, production capacities, and resource availability. Additionally, it involves coordinating with other departments, such as procurement, logistics, and maintenance, to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted production process.
In today’s competitive business environment, production planning plays a vital role in maintaining a competitive edge. It enables organizations to optimize their production processes, reduce lead times, meet customer expectations, and effectively respond to changing market demands. An efficient production planning process can enhance overall productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
In summary, production planning is a critical process that involves creating a detailed roadmap for the production of goods or services. It aims to optimize resources, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery. Effective production planning is essential for businesses to remain competitive and meet customer demands efficiently.

History of Production Planning
The history of production planning dates back to the Industrial Revolution, the foundations of which were laid centuries ago. Before the advent of production planning, production processes were often disorganized and inefficient. This led to wasted resources and production delays.
In the early stages, production planning was primarily a manual and paper-based process, with planners relying on physical documents and charts to track production schedules and materials. However, as technology advanced, so did production planning techniques.
In the early 20th century, manufacturing companies began incorporating more systematic approaches to production planning. The development of assembly lines and mass production techniques, popularized by Henry Ford, revolutionized the manufacturing industry. These advancements paved the way for more structured and organized production planning methods.
With the rise of computers in the second half of the 20th century, production planning underwent a significant transformation. The introduction of computer systems streamlined the planning process, allowing for more accurate forecasting, inventory management, and scheduling.
Over time, production planning has evolved to incorporate various techniques and methodologies such as material requirements planning (MRP), just-in-time (JIT) production, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These advancements have enabled manufacturers to optimize their production processes, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
Today, with the advent of Industry 4.0 and the integration of automation and data analytics, production planning continues to evolve. Concepts such as predictive analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) are being integrated into production planning systems to improve forecasting accuracy, optimize inventory levels, and enhance efficiency.
Overall, the history of production planning has seen a constant drive toward efficiency, organization, and improved decision-making. From manual methods to computerized systems, production planning has played a vital role in the success and growth of manufacturing industries.

Production Planning vs. Production Scheduling
Production planning and production scheduling are both essential components of the production process, but they serve different purposes. Production planning involves creating a detailed roadmap for the entire production process. It includes determining the production capacity, identifying the necessary resources, and setting timelines for each step.
The main purpose of production planning is to ensure that all the necessary resources and materials are available at the right time and in the right quantity. It helps in optimizing production processes, reducing costs, and meeting customer demand efficiently. On the other hand, production scheduling focuses on creating a detailed schedule for each task within the production process. It involves allocating resources, setting start and end times, and coordinating activities to ensure a smooth flow of production.
The main purpose of production scheduling is to optimize the utilization of resources and minimize idle time or bottlenecks in the production process. It helps in managing production priorities, avoiding delays, and meeting delivery deadlines. While production planning focuses on strategic decision-making and long-term planning, production scheduling is more tactical and short-term oriented.
An effective production planning process ensures a seamless flow of materials, reduces waste, and minimizes production delays. Production scheduling, on the other hand, ensures efficient resource allocation, increased productivity, and timely delivery of products. Organizations must have a well-defined production planning and scheduling process in place to optimize their production efficiency, reduce costs, and meet customer demands effectively. Both functions work hand in hand to achieve these objectives.
Why is Production Planning Important?
The importance of production planning are;
- Efficient resource utilization: Production planning plays a crucial role in utilizing resources effectively. By carefully scheduling production activities, companies can minimize wastages, reduce idle time, and optimize the use of raw materials, equipment, and labor.
- Time and cost savings: Effective production planning helps businesses save time and money. By analyzing the production process and identifying bottlenecks or areas for improvement, companies can streamline operations, reduce delays, and avoid unnecessary downtime, resulting in increased productivity and cost savings.
- Meeting customer demands: Production planning ensures that companies can meet customer demands on time. By forecasting demand and developing production schedules accordingly, businesses can avoid stockouts or overproduction, leading to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
- Improved efficiency and productivity: With a well-designed production plan in place, companies can enhance their overall efficiency and productivity levels. It helps in identifying and eliminating unnecessary steps or activities, optimizing workflows, and implementing Lean manufacturing principles, ultimately leading to better output quality and reduced lead times.
- Effective inventory management: Production planning is closely intertwined with inventory management. By accurately forecasting demand and aligning production schedules, businesses can avoid excess inventory levels and the associated costs of storage, obsolescence, and risk of product spoilage.
- Minimization of production disruptions: By proactively planning production activities, companies can mitigate the risk of disruptions such as equipment breakdowns, supply chain issues, or unexpected events. This allows businesses to maintain smooth operations, minimize downtime, and meet production targets consistently.
- Strategic decision-making: Production planning helps businesses make informed strategic decisions. By analyzing production data, trends, and market forecasts, companies can determine optimal production levels, invest in the right equipment and technology, and adapt to changing market conditions more effectively.
In conclusion, production planning is essential for businesses to optimize their resources, save time and costs, meet customer demands, improve efficiency, manage inventory effectively, minimize disruptions, and make informed strategic decisions. By implementing effective production planning practices, companies can gain a competitive edge in the market and achieve long-term success.

Key Components of Production Planning
Production planning is a complex process that involves several key components. These components play a critical role in ensuring the efficient and effective execution of production activities. Here are some of the key components of production planning:
- Demand Forecasting: Demand forecasting is the estimation of the expected future demand for a product or service by analyzing past data. This component is crucial as it helps in determining the quantity and timing of production. Accurate demand forecasting enables businesses to avoid overproduction or underproduction, leading to optimized inventory management and customer satisfaction.
- Capacity Planning: Capacity planning involves determining the production capacity needed to meet the forecasted demand. This component considers various factors such as available resources, production capabilities, and production timeframes. By analyzing capacity requirements, businesses can allocate resources efficiently, avoid bottlenecks, and ensure smooth production operations.
- Production Scheduling: Production scheduling involves creating a detailed plan for executing production tasks within a given timeframe. This component includes allocating resources, setting production sequences, and establishing production timelines. Effective production scheduling helps in balancing workload, minimizing production lead times, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Material Planning and Procurement: Material planning involves determining the types and quantities of materials required for production. It also includes identifying reliable suppliers and establishing procurement strategies. Efficient material planning and procurement ensure that the necessary materials are available when needed, reducing production delays and holding costs.
- Workforce Planning: Workforce planning involves determining the required number of skilled workers and their allocation across various production activities. This component considers factors like production volumes, skill requirements, and labor availability. Well-planned workforce planning ensures that the right workforce is in place to meet production demands and maintain productivity levels.
- Quality Control: Quality control is a crucial component of production planning. It involves establishing processes, standards, and procedures to ensure that the produced goods or services meet the desired quality requirements. Effective quality control helps in detecting and resolving production issues, minimizing defects, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Performance Monitoring and Analysis: Monitoring and analyzing production performance is essential to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions. This component involves gathering and analyzing production data, key performance indicators (KPIs), and other metrics. By continuously monitoring performance, businesses can identify trends, anticipate challenges, and implement corrective measures.
These key components of production planning work together to ensure that production activities are carried out smoothly, efficiently, and with optimal results. By paying attention to each component, businesses can enhance productivity, minimize costs, and achieve their production goals effectively.

The Benefits of Effective Production Planning
Effective production planning brings several benefits to companies. Here are some of the benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: A well-designed production plan ensures that resources, such as materials, labor, and equipment, are used optimally. This leads to increased efficiency in the manufacturing process, reducing waste and improving productivity.
- Enhanced Product Quality: By having a detailed production plan in place, organizations can closely monitor and control each step of the production process. This helps to identify and address any quality issues promptly, resulting in higher product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Lead Time: Efficient production planning enables organizations to streamline their operations, resulting in shorter lead times. By effectively scheduling tasks, coordinating resources, and minimizing bottlenecks, the production cycle can be expedited, allowing products to reach customers faster and improving overall responsiveness.
- Cost Savings: Effective production planning helps in identifying unnecessary steps, minimizing duplication of efforts, and optimizing resource allocation. These efficiencies lead to cost savings in areas such as material procurement, inventory holding, and labor utilization.
- Improved Customer Service: By planning production activities effectively, organizations can ensure that customer orders are fulfilled accurately and on time. This enhances customer satisfaction and builds a positive reputation for the organization in the market.
- Flexibility to Meet Demand: A well-structured production plan enables organizations to handle fluctuations in demand effectively. By forecasting demand patterns and planning production capacity accordingly, they can respond quickly to changing market conditions, avoid stockouts, and maintain customer loyalty.
In summary, effective production planning plays a critical role in maximizing efficiency, improving product quality, reducing lead times, achieving cost savings, enhancing customer service, and enabling organizations to adapt to dynamic market demands. By investing time and resources into production planning, businesses can gain a competitive edge and drive their success in today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape.

Production Planning Process
The production planning process is a systematic approach used by businesses to ensure efficient utilization of resources and meet customer demand. This process involves various stages that are essential for effective production management. Here are the key steps involved in the production planning process:
- Demand forecasting: Production planning begins by estimating future demand based on market trends, customer orders, and historical data. Accurate demand forecasting helps in determining the quantity and type of products to be produced.
- Capacity planning: Once the demand is forecasted, businesses assess their production capacity to determine if it can handle the projected volume. This involves evaluating factors such as equipment availability, workforce capabilities, and production constraints.
- Master production schedule: The master production schedule (MPS) is created to specify the quantity and timing of each product to be manufactured. It is developed by considering demand forecasts, available resources, and production constraints.
- Material planning: Material planning involves determining the quantity and timing of raw materials and components required for production. Businesses need to ensure that the necessary materials are available at the right time to avoid disruptions in the production process.
- Routing and sequencing: Routing involves determining the specific activities and operations required to produce a product, including the order in which these activities should be performed. Sequencing determines the best order in which to produce different products to optimize efficiency.
- Production scheduling: Once the routing and sequencing are determined, a detailed production schedule is created. This schedule outlines each production activity’s start and end times, ensuring that production flows smoothly and meets deadlines.
- Procurement and purchasing: The procurement and purchasing department is responsible for procuring the required materials, components, and equipment needed for production. This involves selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing the supply chain efficiently.
- Execution and monitoring: Once the production process begins, it is essential to monitor the progress and ensure that it aligns with the planned schedule. Any deviations or bottlenecks should be identified and addressed promptly to maintain production efficiency.
- Quality control: Quality control measures must be implemented throughout the production process to ensure that products meet the required standards. Each production system has its specific quality control steps.
- Continuous improvement: The production planning process is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regular evaluation and analysis of production data can help identify opportunities for improvement, including reducing costs, enhancing efficiency, and optimizing resource utilization.
By following the production planning process, businesses can streamline their production operations, minimize lead times, reduce inventory carrying costs, and meet customer demands effectively. It allows for better utilization of resources and facilitates the smooth flow of operations, ultimately leading to increased profitability and customer satisfaction.
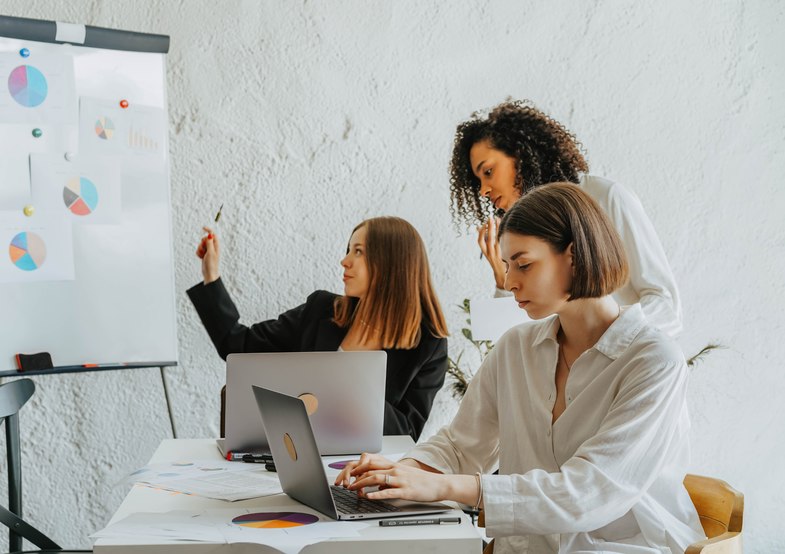

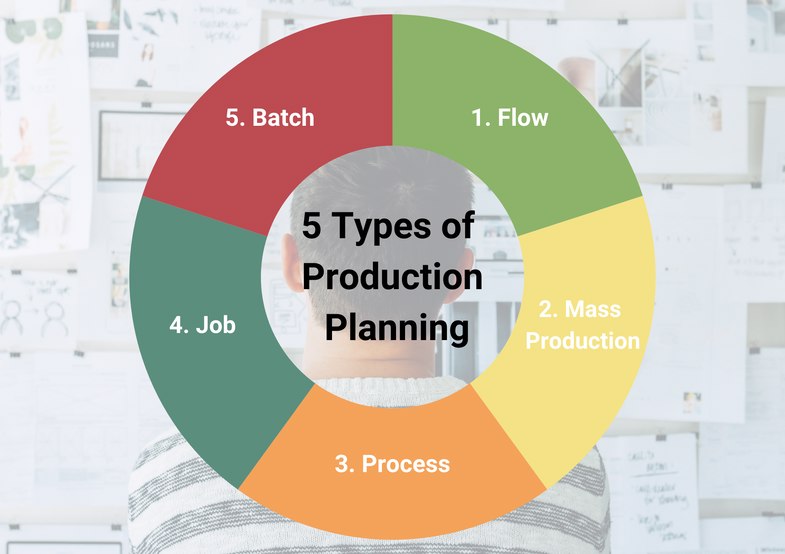
5 Types of Production Planning
The 5 types of production planning are;
1) Flow
The flow method focuses on optimizing the production flow by eliminating bottlenecks and delays between production stages and steps. It often requires the implementation of strict standardization and rigorous quality control measures. This approach is particularly suitable for products that need to be produced individually rather than in batches unless customized designs are required for each product. When preparing for flow production, it is crucial to consider inventory management to avoid potential delays throughout the process.
2) Mass Production
The mass production method is almost identical to the flow method. Both methods are very similar. However, it usually involves more automation and specialized production lines for one product. The aim is to minimize the time required for product changeover and to produce larger quantities of products quickly. Unlike batch production, mass production does not require products to go through specific stages in batches. Therefore, it is important to accurately estimate the potential demand for the product when preparing for mass production. Although mass production can produce many products quickly, careful planning can avoid excess inventory.
3) Process
Process production aims to ensure a seamless transition between production stages by applying a significant degree of automation. This is particularly beneficial for liquid substances that are not sold as individual products. Since defects can have a rapid and significant impact on the overall product, process manufacturing requires diligent monitoring at every stage to maintain high quality standards. Production planning can include the allocation of personnel and equipment to closely monitor the product throughout the process.
4) Job
Job production planning involves detailed planning and production procedures customized for each individual product. Also known as project-based production, this method is particularly suitable for personalized products. Unlike automated production processes, the planning phase for job production can be accelerated depending on the specific task. By outlining the process in advance, small businesses can effectively anticipate and address potential obstacles, thus ensuring smooth operations.
5) Batch
Batch production planning relies on group production as a vital component. Producing products in batches allows each production stage to be closely monitored and managed. This method also allows for quick corrections, as errors found in one batch can be corrected before moving on to the next. However, it is important to consider the capacity of the production equipment at each stage to avoid bottlenecks or delays caused by different processing capacities. Therefore, careful consideration of capacity is crucial in batch production planning.
How to Production Planning?
Production planning is generally done with the following steps;
- Analyze the Demand: Start by analyzing the demand for your product or service. Consider factors such as customer preferences, market trends, and seasonality. This will help you estimate the required production volume and plan accordingly.
- Create a Master Production Schedule: Develop a master production schedule that outlines the production quantities and schedules for each product. This schedule should take into account available resources, production capacity, and any constraints or limitations.
- Determine Inventory Levels: Assess your inventory levels to ensure that you have sufficient raw materials and finished goods to meet production demands. Optimize your inventory by balancing the costs of carrying inventory with the risks of stockouts.
- Allocate Resources: Allocate resources, such as machinery, equipment, and labor, based on the production schedule. Consider the availability and capabilities of your resources to ensure efficient production.
- Coordinate with Suppliers: Collaborate with suppliers to ensure a smooth supply chain. Communicate your production requirements, lead times, and quality standards to suppliers so that they can deliver the necessary materials on time.
- Optimize Production Processes: Continuously review and optimize your production processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Use tools like lean manufacturing techniques, Six Sigma, or automation to streamline operations.
- Implement Quality Control: Implement robust quality control measures to ensure that your products meet the required standards. Perform regular inspections, tests, and audits to identify and rectify any quality issues.
- Monitor and Track Progress: Regularly monitor and track the progress of your production planning. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure productivity, efficiency, and adherence to schedules. Make the necessary adjustments and corrections to optimize production.
By following these steps, you can develop a comprehensive production plan that ensures smooth operations, efficient resource utilization, and timely delivery of products to meet customer demands.

Common Production Planning Mistakes
1) Poor Demand Forecasting
One of the most common mistakes in production planning is inaccurate demand forecasting. If a company underestimates demand, it may result in stockouts and lost sales. On the other hand, overestimating demand can lead to excess inventory and increased carrying costs. To avoid this mistake, it is crucial to gather and analyze accurate historical sales data, market trends, and customer feedback to make informed demand forecasts.
2) Inefficient Resource Allocation
Another common mistake is a failure to effectively allocate resources. Production planning involves coordinating various resources such as labor, materials, equipment, and facilities. Inefficient resource allocation can result in bottlenecks, increased production costs, and missed deadlines. To avoid this, companies should conduct a thorough analysis of their resources, identify any constraints, and allocate them optimally to meet production requirements.
3) Inadequate Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is essential for ensuring that production capacity aligns with demand. Some businesses make the mistake of not adequately analyzing their current and future capacity requirements. As a result, they may encounter capacity shortages during peak periods or have excess capacity during slower periods. By conducting regular capacity assessments and implementing strategies like hiring temporary staff or outsourcing, businesses can better match capacity to demand fluctuations.
4) Lack of Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration among different departments involved in production planning are crucial for smooth operations. Lack of communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and production inefficiencies. It is essential to establish clear channels of communication, share relevant information, and encourage collaboration to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
5) Failure to Account for Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken for an order to be fulfilled from the moment it is placed. It includes order processing, manufacturing, and delivery time. Neglecting to account for lead time can result in delayed deliveries and dissatisfied customers. It is important to accurately estimate lead times for each stage of the production process to ensure that orders are fulfilled on time.
Avoiding these common production planning mistakes can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. By implementing effective production planning strategies and continuously monitoring and adapting them, businesses can optimize their production processes and achieve their goals.
Videos Related to Production Planning
We would like to suggest you a video about Production Planning. You can learn about production planning by watching this video. You can click HERE for more videos.
